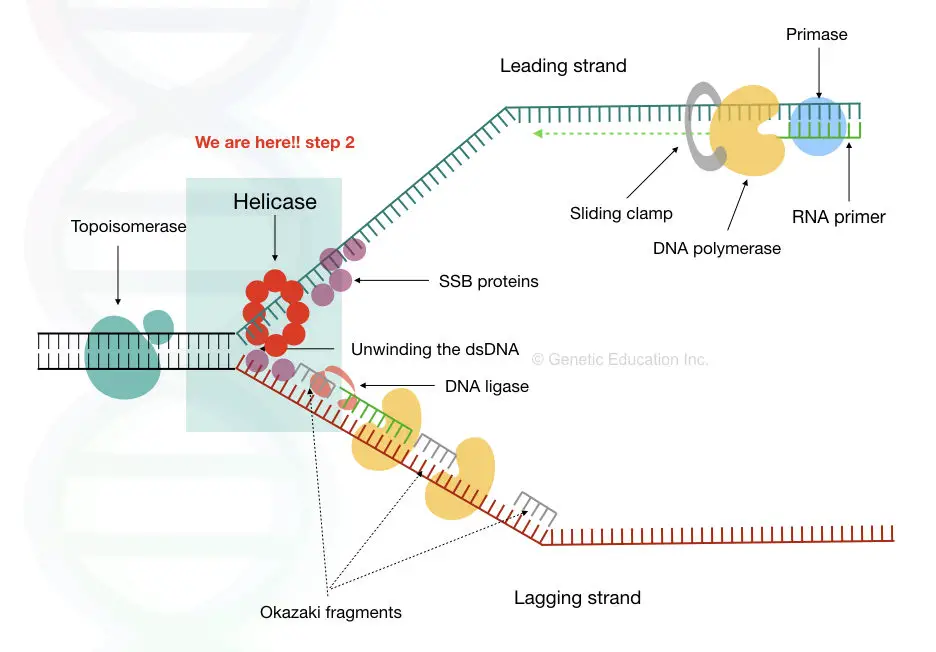
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template - It uses atp to unwind the dna template. What class of enzymes relieve. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. The dna polymerase enzyme, responsible for synthesizing the new dna strand, requires atp to initiate and extend the replication fork. When helicases bind atp, they undergo conformational changes that facilitate movement along the. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. By unwinding the dsdna, it separates. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. Dna helicases are enzymes characterized by the presence of conserved motifs involved in atp binding, atp hydrolysis and translocation along the dna strand. Coli contains a subunit called the b subunit, which dramatically increases the enzyme's. For example, dna helicase uses atp. Replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication, recognized by initiator proteins that unwind the dna helix, creating a replication fork where the template. The dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Relieves coiling in dna strands ahead of the replication fork. What class of enzymes relieve. During dna replication, the _________ strand is synthesized continuously while the _________ strand is synthesized. Causes dna strand separation at the origin or replication. Match these enzymes involved in dna replication with their function. A dna helicase acts at the front edge of the fork to unwind the dna. Additionally, helicases, which unwind the double helix,. It binds to the rna at a rho utilisation (rut) site, which is rich in. Learn how atp hydrolysis fuels this process, and explore the intricate. Relieves coiling in dna strands ahead of the replication fork. For example, dna helicase uses atp. It uses atp to unwind the dna template. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. Replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication, recognized by initiator proteins that unwind the dna helix, creating a replication fork where the template. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. The dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. The dna polymerases are present on both the. The dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Relieves coiling in dna strands ahead of the replication fork. Discover how enzymes utilize atp to unwind dna. In the replisome, the ______ is composed of primase, helicase, and accessory proteins that prime the lagging strand. When helicases bind atp, they undergo conformational changes that facilitate movement along the. In the replisome, the ______ is composed of primase, helicase, and accessory proteins that prime the lagging strand. Learn how atp hydrolysis fuels this process, and explore the intricate. The dna polymerases are present on both the leading and lagging strands, synthesizing the nascent dna strands. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzymes that use energy from. During dna replication, the _________ strand is synthesized continuously while the _________ strand is synthesized. Additionally, helicases, which unwind the double helix,. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. The dna polymerase enzyme, responsible for synthesizing the new dna strand, requires atp to initiate and extend the replication fork. Atp hydrolysis provides the energy required for helicases. Relieves coiling in dna strands ahead of the replication fork. The enzyme _______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. For example, dna helicase uses atp. Atp hydrolysis provides the energy required for helicases to unwind the dna double helix. The dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. A dna helicase acts at the front edge of the fork to unwind the dna. The dna polymerase enzyme, responsible for synthesizing the new dna strand, requires atp to initiate and extend the replication fork. Causes dna strand separation at the origin or replication. Learn how atp hydrolysis fuels this process, and explore the intricate. The dna polymerase iii enzyme. Replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication, recognized by initiator proteins that unwind the dna helix, creating a replication fork where the template. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzymes that use energy from atp to unwind the dna template are called what, discontinuous synthesis on the lagging. Atp hydrolysis provides the energy required for. The dna polymerases are present on both the leading and lagging strands, synthesizing the nascent dna strands. The enzyme _______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. Discover the crucial role of enzymes in unwinding dna templates, enabling genetic material to be accessed and copied. In the replisome, the ______ is composed of primase, helicase, and accessory proteins that prime. All dna polymerases require a short strand of dna or rna, called a____ to begin their synthesis. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. During dna replication, the _________ strand is synthesized continuously while the _________ strand is synthesized. More experiments are required to reconcile these differences, but a potential explanation could be that dna templates used. What class of enzymes relieve. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. By unwinding the dsdna, it separates. The dna polymerases are present on both the leading and lagging strands, synthesizing the nascent dna strands. In the replisome, the ______ is composed of primase, helicase, and accessory proteins that prime the lagging strand. More experiments are required to reconcile these differences, but a potential explanation could be that dna templates used in the in vitro assays do not fully recapitulate. The enzyme ______ uses atp to unwind the dna template. All dna polymerases require a short strand of dna or rna, called a____ to begin their synthesis. Match these enzymes involved in dna replication with their function. It uses atp to unwind the dna template. Relieves coiling in dna strands ahead of the replication fork. A dna helicase acts at the front edge of the fork to unwind the dna. Replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication, recognized by initiator proteins that unwind the dna helix, creating a replication fork where the template. Helicases are enzymes that separate the dna strands during dna replication by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Learn how atp hydrolysis fuels this process, and explore the intricate.The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
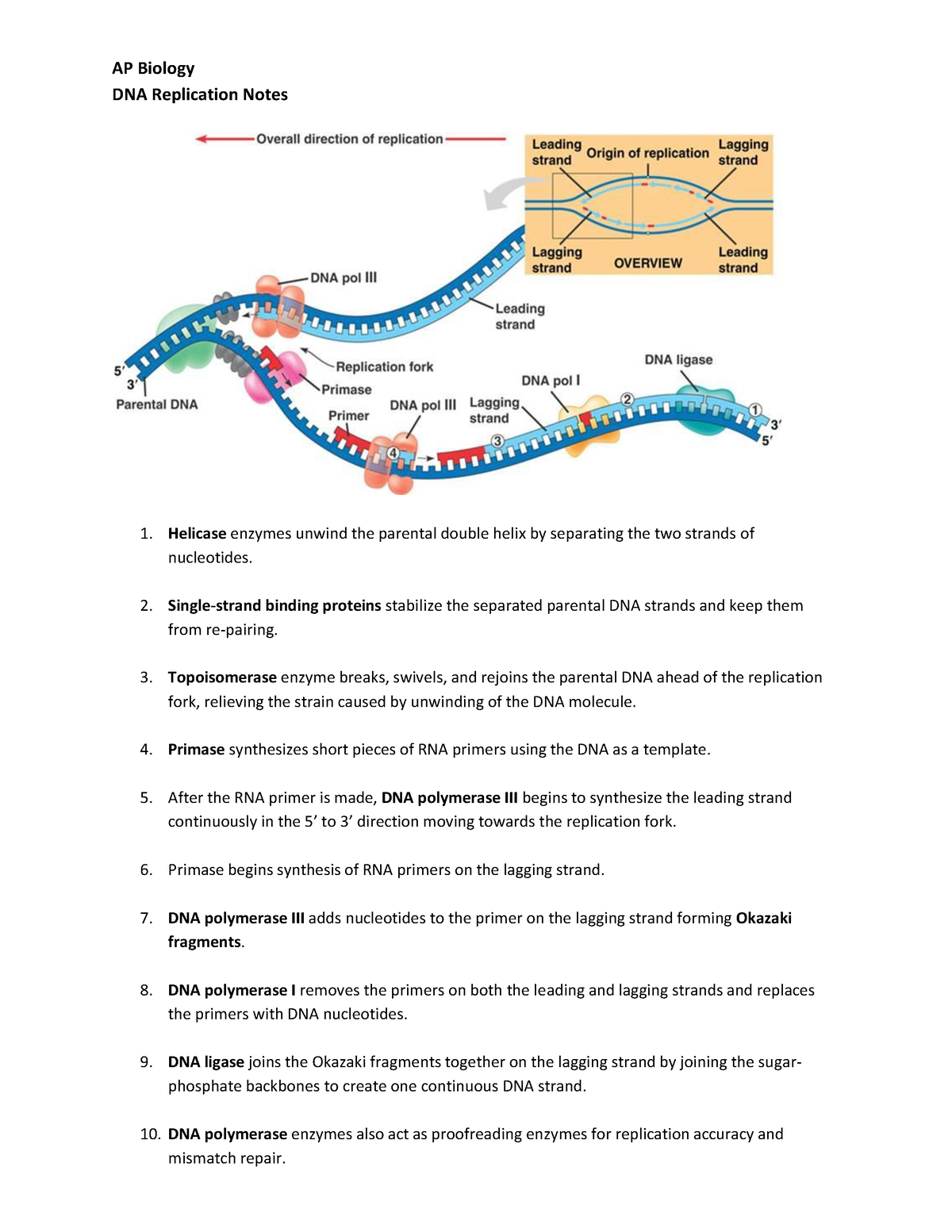
Steps of DNA Replication Notes AP Biology DNA Replication Notes
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
A model of helicase function to unwind or rewind doublestranded
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
It Binds To The Rna At A Rho Utilisation (Rut) Site, Which Is Rich In.
The Enzyme _______ Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template.
Atp Hydrolysis Provides The Energy Required For Helicases To Unwind The Dna Double Helix.
Causes Dna Strand Separation At The Origin Or Replication.
Related Post: